
Stock Trading for Beginners: Lesson 3 – Building and Managing a Diversified Stock Portfolio
05 September 2023
203 views
Introduction to Portfolio Diversification
Diversification is a key strategy in stock investing that involves spreading your investments across different assets to reduce risk. A well-diversified portfolio can help protect your investments from market volatility and improve your chances of achieving stable returns.
Why Diversify?
- Risk Reduction: Diversifying reduces the impact of a poor-performing investment on your overall portfolio.
- Potential for Higher Returns: A mix of different asset classes can capture growth opportunities in various sectors.
- Stability: Diversification can provide more consistent returns over time by balancing gains and losses across different investments.
Steps to Build a Diversified Portfolio
1. Determine Your Investment Goals and Risk Tolerance
Understanding your financial goals and risk tolerance is the first step in building a diversified portfolio.
- Goals: Define what you want to achieve with your investments (e.g., retirement, education, wealth growth).
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your ability to withstand market fluctuations. Are you a conservative, moderate, or aggressive investor?
2. Choose Asset Classes
Invest in a variety of asset classes to achieve diversification. Common asset classes include:
- Stocks: Ownership in companies.
- Large-Cap Stocks: Established companies with a market capitalization of over $10 billion.
- Mid-Cap Stocks: Companies with a market capitalization between $2 billion and $10 billion.
- Small-Cap Stocks: Companies with a market capitalization below $2 billion.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations.
- Real Estate: Investments in property or real estate investment trusts (REITs).
- Commodities: Physical assets like gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products.
3. Select Individual Stocks
Choose individual stocks that align with your investment strategy and goals.
- Growth Stocks: Companies expected to grow at an above-average rate.
- Value Stocks: Undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.
- Dividend Stocks: Companies that pay regular dividends, providing income.
4. Allocate Assets
Allocate your investment capital across different asset classes and individual stocks based on your goals and risk tolerance.
- Aggressive Portfolio: Higher allocation to stocks, particularly growth and small-cap stocks.
- Moderate Portfolio: Balanced allocation between stocks and bonds, with a mix of growth and value stocks.
- Conservative Portfolio: Higher allocation to bonds and dividend stocks for stability and income.
5. Regularly Review and Rebalance
Monitor your portfolio regularly to ensure it stays aligned with your goals and risk tolerance. Rebalance your portfolio by adjusting the asset allocation to maintain your desired level of risk and return.
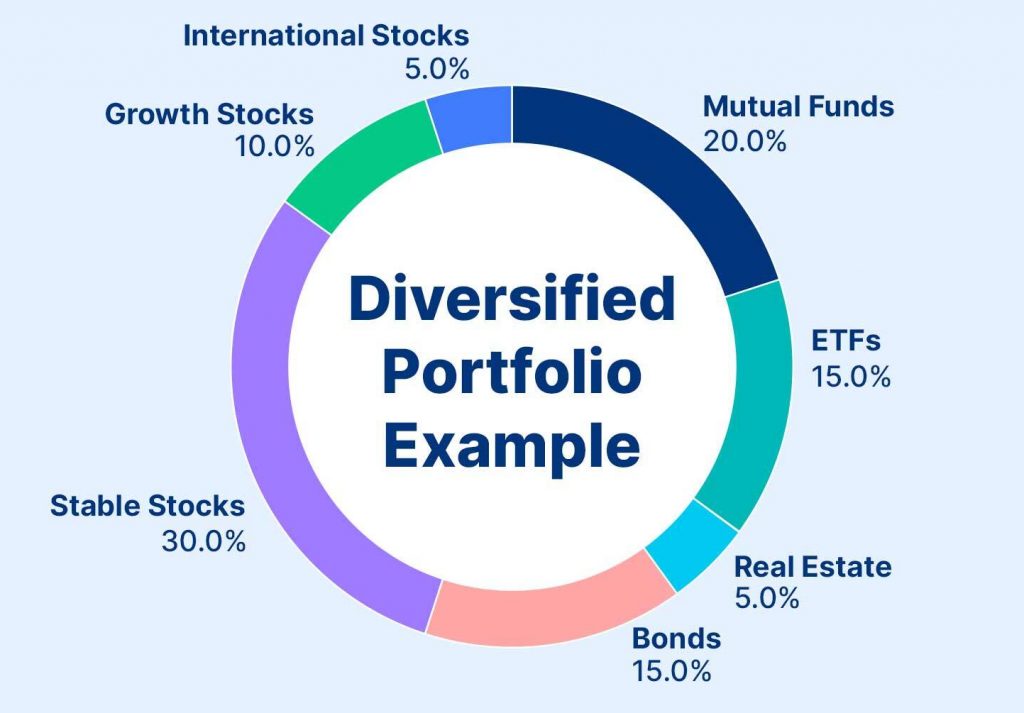
Practical Example
- Scenario: You have $10,000 to invest and want to build a diversified portfolio.
- Steps:
- Determine Goals and Risk Tolerance: Your goal is wealth growth over 10 years, and you have a moderate risk tolerance.
- Choose Asset Classes:
- Allocate 60% ($6,000) to stocks.
- Allocate 30% ($3,000) to bonds.
- Allocate 10% ($1,000) to real estate (REITs).
- Select Individual Stocks:
- Growth Stocks: Invest $2,000 in technology and healthcare companies.
- Value Stocks: Invest $2,000 in consumer goods and financial companies.
- Dividend Stocks: Invest $2,000 in utilities and telecommunications companies.
- Allocate Assets: Distribute your investment capital according to your chosen asset classes and individual stocks.
- Review and Rebalance: Check your portfolio quarterly to ensure it aligns with your goals and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
Building and managing a diversified stock portfolio is essential for reducing risk and achieving consistent returns. By understanding your goals and risk tolerance, choosing a variety of asset classes, selecting individual stocks, and regularly reviewing and rebalancing your portfolio, you can create a robust investment strategy.
With these foundational lessons, you are now equipped to start your journey in stock investing with confidence. Continue learning, stay informed about market trends, and refine your strategy as you gain more experience.




