
Forex Mastery: Lesson 2 – Risk Management and Portfolio Optimization
30 November 2023
241 views
Introduction to Advanced Risk Management
Advanced risk management techniques are crucial for safeguarding your capital and ensuring long-term success in forex trading. In this lesson, we will explore sophisticated methods to manage risk and optimize your trading portfolio.
Diversification
Diversification involves spreading your investments across multiple assets to reduce risk. In forex trading, this means trading different currency pairs to mitigate the impact of adverse movements in any single pair.
Key Concepts
- Correlation: Understand the correlation between different currency pairs. Pairs that are positively correlated move in the same direction, while negatively correlated pairs move in opposite directions.
- Asset Allocation: Allocate your capital across various currency pairs based on their correlation and your risk tolerance.
Example
- Trading both EUR/USD and USD/CHF can reduce risk since these pairs often move in opposite directions (negative correlation).
- Allocating capital to both pairs balances potential losses and gains.
Hedging Strategies
Hedging involves opening positions in different markets to offset potential losses in your primary trades. This strategy protects your capital from significant market movements.
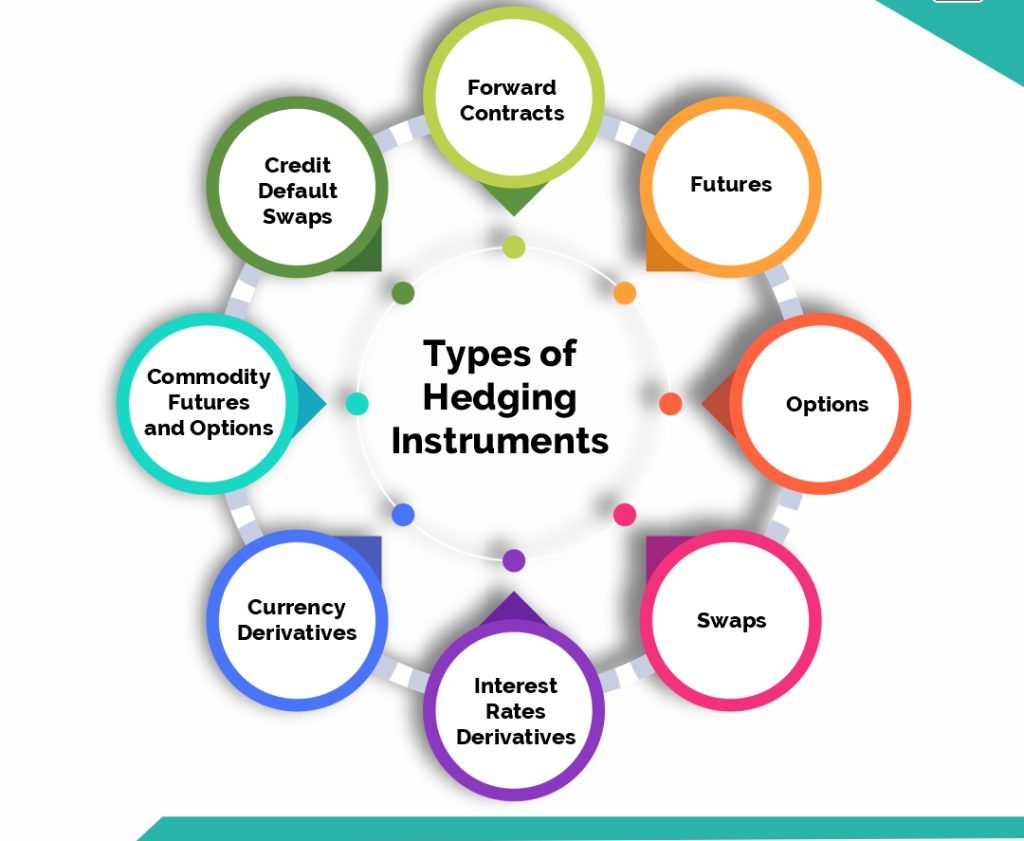
Key Concepts
- Direct Hedging: Open a position in the opposite direction of your initial trade within the same currency pair. For example, if you are long EUR/USD, you can hedge by opening a short EUR/USD position.
- Indirect Hedging: Open a position in a correlated currency pair. For instance, if you are long GBP/USD, you can hedge with a short position in EUR/USD.
Example
If you are long USD/JPY and the market becomes volatile, you can hedge by opening a short position in USD/CHF. This indirect hedge protects your position if the USD weakens.
Risk-Adjusted Return
Risk-adjusted return measures the potential return of an investment relative to its risk. This concept helps you evaluate and optimize your trading strategies for better performance.
Key Concepts
- Sharpe Ratio: Calculates the risk-adjusted return by comparing the portfolio return to the risk-free rate and adjusting for volatility. A higher Sharpe Ratio indicates a better risk-adjusted return.
- Sortino Ratio: Similar to the Sharpe Ratio but focuses only on downside risk. A higher Sortino Ratio indicates a better risk-adjusted return, particularly in avoiding losses.
Example
If your trading portfolio has an annual return of 12%, a risk-free rate of 2%, and a standard deviation of 10%, the Sharpe Ratio would be 1.0. This indicates a reasonable risk-adjusted return.
Position Sizing Techniques
Advanced position sizing techniques help manage risk by determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade.
Key Concepts
- Kelly Criterion: A method to determine the optimal size of a series of bets to maximize long-term wealth. It involves balancing the probability of winning with the odds received.
- Fixed Fractional: Allocate a fixed percentage of your trading capital to each trade, typically between 1-2%. This ensures consistent risk management.
Example
If you have a $10,000 trading account and you use the fixed fractional method with 2% risk per trade, you would risk $200 per trade.
Practical Application
- Evaluate Correlations: Use a correlation matrix to understand the relationship between different currency pairs.
- Implement Hedging: Apply direct or indirect hedging strategies to protect your positions.
- Calculate Risk-Adjusted Returns: Use the Sharpe Ratio and Sortino Ratio to evaluate your trading performance.
- Optimize Position Size: Apply the Kelly Criterion or fixed fractional method to determine your position size.
Example Scenario
- Scenario: You have a $50,000 trading account and want to diversify your portfolio while managing risk.
- Response:
- Identify three currency pairs with low correlation: EUR/USD, AUD/JPY, and GBP/CHF.
- Allocate 30% of your capital to EUR/USD, 30% to AUD/JPY, and 40% to GBP/CHF.
- Use direct hedging by opening a short position in EUR/USD if the market shows signs of a downtrend.
- Calculate the Sharpe Ratio of your portfolio to ensure a high risk-adjusted return.
- Determine position sizes using the Kelly Criterion, ensuring you do not risk more than 2% of your capital on any single trade.
Conclusion
Advanced risk management and portfolio optimization techniques are essential for successful forex trading. By diversifying your trades, implementing hedging strategies, evaluating risk-adjusted returns, and optimizing position sizes, you can enhance your trading performance and protect your capital.
In the next lesson, we will explore algorithmic trading and quantitative analysis.




